Alt-R™ HDR Donor Blocks for CRISPR Knock-In Experiments
Built for homology-directed repair experiments
For researchers looking to accelerate their CRISPR, HDR-mediated insertions (>120 bases), IDT dsDNA templates offer a cost effective, high-fidelity option to reduce the amount of downstream screening via higher HDR rates and lower unintended integrations.
Ordering
- Ideal for making longer than 120 bp genomic insertions
- Sequence-verified via next generation sequencing
- Modified to increase successful HDR events
- Lower unintended and non-homologous (blunt) integrations
Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks
HDR Donor Blocks include chemical modifications within universal, non-integrating terminal sequences to help reduce unwanted blunt integration events.
Alt-R HDR Design Tool
If you don’t have a template design of your own, use our Alt-R HDR Design Tool to design your template. Simply provide basic information about your target site, and then use the tool to design and visualize your desired edit within the sequence. The Alt-R HDR Design Tool will provide the recommended HDR donor template along with gRNA(s) for your specifications.
Alt-R™ HDR Enhancer Protein
Alt-R HDR Enhancer Protein is a novel protein-based reagent that promotes homology-directed repair by inhibiting 53BP1, a key regulator of dsDNA break repair pathway choice. It improves editing efficiency by up to 2X across established and hard-to-edit primary cells (iPSCs, HSPCs) without increasing off-target effects, genomic translocations, or compromising cell viability. Compatible with multiple CRISPR systems, including Cas9, Cas12a, and Eureca™-V, it integrates seamlessly into existing workflows. Offered in RUO format with a cGMP grade coming soon, Alt-R HDR Enhancer Protein is specifically engineered for translational researchers advancing CRISPR-based therapeutics.
Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2
Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 is a small molecule compound that increases homology-directed repair by blocking the NHEJ pathway. Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 exhibits its activity in multiple cell lines, including both adherent and suspension cell lines. Its activity is independent of the enzyme employed; for example, it can be used either with Alt-R S.p. Cas9 nucleases or A.s. Cas12a (Cpf1) nucleases. This versatile reagent is also compatible with electroporation and lipofection methods. When you combine Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 and Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks you significantly increase your large insert KI rates and reduce the rate of non-homologous (blunt) integrations at off-target DSBs. See below data for details.
Request a consultation
Have questions for our experts? Your time is valuable and we’ll prioritize your inquiry. Click on “Request a consultation” to provide brief information about your project, and we’ll be in touch to discuss it ASAP.
Request a consultationProduct details
Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks were developed to address the need for better HDR research solutions when creating larger changes or inserts in the genome. Utilizing the same high-fidelity process as IDT gBlocks™ HiFi Gene Fragments, the HDR Donor Blocks incorporate advanced chemical modifications at each end of the sequence to boost HDR rates and aid in inhibiting the occurrence of blunt-end integration of the donor sequence. In addition, universal sequences are added to the ends of the sequence ordered to provide consistency and speed of production.
Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks are available from 201 to 3000 bases in length and are generated from clonally purified DNA. The donors are sequence-verified via next generation sequencing and are typically shipped in as few as 17 business days*. They are composed of A, T, G, and C nucleotides only. Sequence information is always secure and confidential at IDT. Non-disclosure agreements are available through IDT legal services upon request.
* The time required to manufacture an Alt-R HDR Donor Block is dependent on many factors and in a few cases may exceed the estimated delivery time.
Product data
Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks offer an improved solution for efficient generation of large knock-ins compared to long, single-stranded DNA templates
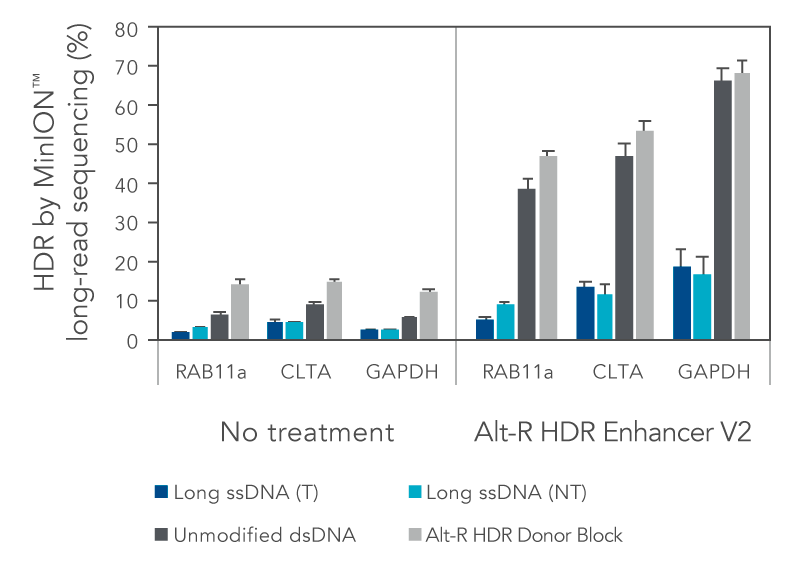
We investigated the HDR efficiency of inserting a green fluorescent protein (GFP) tag using either long, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) templates (700 bp insert, 200 bp homology arms). The combined use of the modified Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks and the Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 gave the higher HDR rates compared to no treatment when tested at multiple genomic loci and in multiple cell lines (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks offer improved large knock-in rates relative to long ssDNA HDR templates. HEK-293 and K562 cells were electroporated with 2 µM Cas9 RNP complexes targeting three genomic loci (RAB11a, CLTA, and GAPDH) along with 50 nM dsDNA or ssDNA donor templates using the Nucleofector™ system (Lonza). HDR templates were designed to mediate a GFP-tagging event (700 bp insert, 200 bp homology arms). The dsDNA templates contained either no modifications (unmodified), or the Alt-R HDR Donor Block modification. Both the targeting (T) and non-targeting (NT) strands were tested for the long ssDNA templates. After electroporation, cells were plated in media with or without 1 µM Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 with a media change after 24 hours. Genomic DNA was isolated 48 hours after electroporation. Editing was assessed by long-read amplicon sequencing on the MinION™ system (Oxford Nanopore Technologies) using R9.4.1 chemistry and Guppy High Accuracy (HAC) basecalling. Reads were mapped to the unedited reference amplicon or desired HDR outcome using minimap2 (-x map-ont). A read was classified to be derived from the HDR pathway if it preferentially mapped to the desired HDR outcome. HDR efficiency was measured by calculating the read counts classified as HDR relative to the total aligned reads per sample. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM).
Combined use of Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks and Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 assists in mitigating the risk for off-target integration events
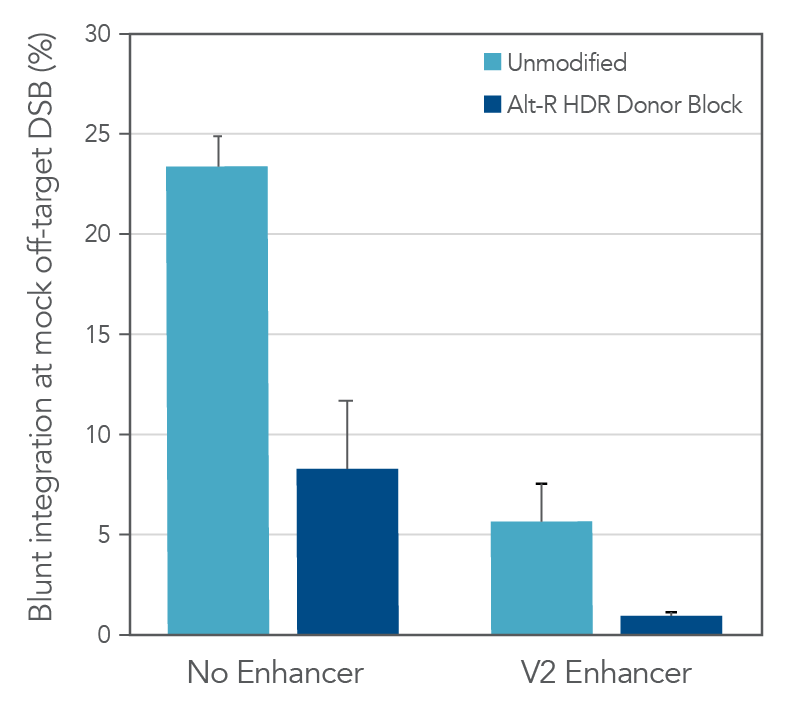
The use of unmodified dsDNA templates poses a risk for unwanted off-target integrations, where the donor is directly ligated into either a double-strand break (DSB) resulting from a Cas9 off-target editing event, or a naturally occurring endogenous DSB. We explored the ability of the Alt-R HDR Donor Block modification to reduce the occurrence of this unwanted repair event by generating a mock off-target DSB. Unmodified or Alt-R modified dsDNA templates for four unique HDR events were co-delivered with a Cas9 RNP targeting a site lacking homology to the donor templates. The combined use of Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks and the Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 substantially reduced the rates of integration at a non-homologous DSB, as compared to no treatment (Figure 2).
Total editing at the mock off-target site was >90% (data not shown). As such, the reported data represent much higher integration frequencies than would be expected at true Cas9 off-targets, or at endogenous DSBs where overall editing frequencies would be lower. Any strategies that reduce the risk for Cas9 off-target editing (such as use of Alt-R HiFi Cas9 Nuclease) further mitigate the risk for off-target integration of the HDR template.
Figure 2. Combined use of Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks and Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 reduces the rate of non-homologous (blunt) integrations at off-target DSBs. A mock off-target DSB was generated by delivering 2 µM Cas9 RNP targeting the SERPINC1 locus into HEK-293 cells using the Nucleofector™ system (Lonza). The dsDNA donor templates mediating GFP insertions at alternative genomic loci (50 nM dose, n = 4 sequences) were co-delivered with the mock off-target RNP. After electroporation, cells were plated in media with or without 1 µM Alt R HDR Enhancer V2 with a media change after 24 hours. Genomic DNA was isolated 48 hours after electroporation. The SERPINC1 locus was PCR-amplified and blunt insertion events were measured by size discrimination on a Fragment Analyzer (Agilent). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM).
Use of optimal homology arm lengths improved HDR efficiency
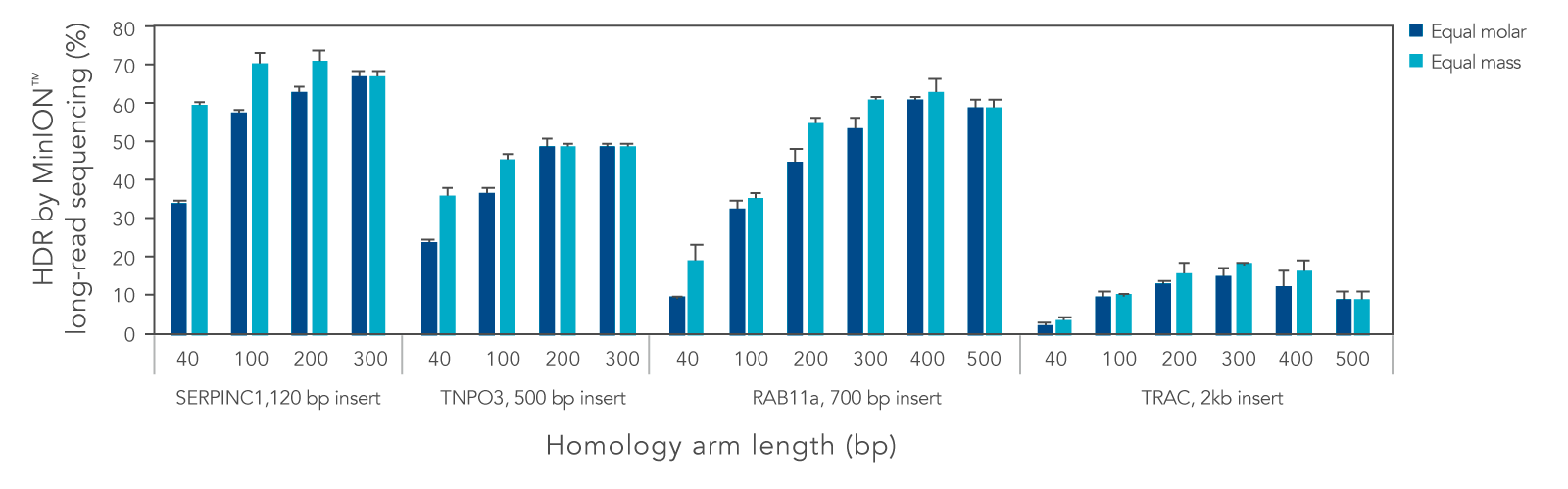
We systematically varied the homology arm length for Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks mediating insertions ranging from 120 to 2000 bp at different genomic loci. Overall, HDR efficiency was improved when using homology arm lengths of 200–300 bp (Figure 3). While HDR rates varied with site and insertion size, use of Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks and Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 led to efficient knock-in of sequences up to 2000 bp. Additional design recommendations for HDR templates can be found in the application note “Optimized methods for CRISPR-Cas9 homology-directed repair (HDR) for efficient, high-fidelity genome editing.”
Figure 3. Homology arm lengths of 200–300 bp result in the highest HDR efficiency when using Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks. K562 cells were electroporated with 2 µM Cas9 RNP complexes targeting four genomic loci and Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks mediating 120, 500, 700, or 2000 bp insertions using the Nucleofector™ system (Lonza). Donor templates were designed with homology arm lengths varying from 40 bp up to 500 bp, and were delivered at equal molar or equal mass amounts (100 nM or 1.2 µg for 120 bp insert, 50 nM or 0.9 µg for 500 bp insert, 50 nM or 1.5 µg for 700 bp insert, and 25 nM or 1.3 µg insert for 2000 bp insert). After electroporation, cells were plated in media with or without 1 µM Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 with a media change after 24 hours. Genomic DNA was isolated 48 hours after electroporation. Editing was assessed by long-read amplicon sequencing on the MinION™ system (Oxford Nanopore Technologies) as previously described (Figure 1). Error bars represent the standard deviation of two biological replicates.
Resources
Frequently asked questions
Why are the standard NGS reports of the Alt-R™ HDR Donor Blocks of 2000 base pairs or shorter, titled differently than those longer than 2000 base pairs?
Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks offer a low-cost, high-fidelity option to create CRISPR-mediated insertions. We attain high fidelity by first creating a plasmid-derived clonal product which is confirmed to be correct by the standard NGS verification of this intermediate. This NGS is performed on every HDR block.
The next steps of processing are slightly different depending on the length of the sequence. The method used for sequences shorter than 2000 bp helps IDT to produce the items with a slightly faster turnaround time; while the method used for sequences longer than 2000 bp helps IDT to produce items that have similar success and on-time delivery rates as our shorter products.
Why does IDT offer an additional NGS service for the Alt-R™ HDR blocks?
Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks offer a low-cost, high-fidelity option to create CRISPR-mediated insertions. We attain high-fidelity by creating a plasmid-derived clonal product which is confirmed to be correct by a standard NGS verification of this intermediate. This NGS analysis is performed on every HDR block. The final stage of production creates a linear product with modified ends using IDT’s proprietary method. Based on the hundreds of items produced and tested with this method we see no detectable difference between the sequence composition of the intermediate and the sequence composition of the final product. For most of our customers the additional cost and time associated with an additional round of sequencing is not useful.
For customers who wish to have an added level of quality control we offer an optional NGS service on the final product. This optional QC adds approximately 3 business days to the turnaround time and costs an additional $95 USD within the US, or the equivalent in your local currency.
What should I do if the IDT online ordering tool says that my Alt-R HDR Donor Block is too complex to order?
For most cases, high complexity means that our system has found a region with either very high GC content or several small repeats that would prevent proper synthesis. For Alt-R™ HDR Donor Block sequences with high complexity, we recommend taking the following steps:
- Check your desired insertion for regions of high GC content or repeat elements. If possible, alter any coding regions with complexity issues through codon optimization.
- Check the homology arms for GC content and repeat elements and, where possible, alter the homology arm length to avoid problematic regions. While 200-300 bp homology arm lengths are recommended for optimal HDR efficiency, homology arms as short as 100 bp may be used.
- If these approaches do not resolve the complexity issues, contact us at applicationsupport@idtdna.com for further assistance with your Alt-R HDR Donor Block design.
Is the Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 compatible with Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks?
Yes, the Alt-R™ HDR Enhancer V2 is compatible with the Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks.
Learn more about using the Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 and the HDR Donor Blocks in the Alt-R Donor Blocks protocol.
What are the modifications to the ends of Alt-R™ HDR blocks and what is their purpose?
Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks have additional sequence and chemical modifications to both ends of the ordered sequence that improve the on-target capabilities and integration efficiency relative to unmodified double stranded DNA. The exact nature of the modifications is an IDT proprietary technology that reduces or prevents the insertion of donor DNA via non homologous end joining (NHEJ). NHEJ is a nonspecific and error prone DNA cellular repair method. When unmodified double-stranded DNA is used as donors, this repair mechanism can lead to duplicated sequence errors at the targeted site as well as nonspecific integration elsewhere within the genome.
The modifications to IDT’s Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks occur in the 29 or 30 bases of sequence that are added to each end of the sequence ordered. While the modifications are proprietary, the sequences themselves are available upon request. These sequences have been confirmed to be absent from human and most other mammalian species and are not observed to integrate into the genomes via HDR.
It should also be noted that the universal ends will not be sequenced as these are not part of the customer's design, nor do they integrate into the genome during HDR.
Univ 5´ GTCGTACCGACTGGTAGATGACAGCAAACC
Univ 3´ GATCCGAAAACGGGCGTATAGTCGAGACC
What is the difference between Alt-R™ HDR Donor Blocks and Megamer™ Single-Stranded DNA Fragments?
Important Update: Megamer™ Single-Stranded DNA Fragments were discontinued on December 31, 2025. The following information is provided for reference purposes only.
The Alt-R HDR Donor Block and Megamer products are both intended to generate CRISPR-mediated insertions. Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks are chemically modified dsDNA repair templates while Megamer Single-Stranded DNA Fragments are long ssDNA repair templates. Megamer fragments are also chemically modified templates, however, their modification is different than that of HDR Donor Blocks. Due to the differences in manufacturing, Megamers are limited in yield (3 µg standard) and can be more costly. Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks are available at larger yields that are typically required for cell culture work (3 or 10 µg standard) and offer a more cost-effective solution. While both products can be used to create CRISPR knock-ins, several differences in repair outcomes have been observed between dsDNA and ssDNA repair templates.
First, ssDNA innately has a lower risk of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) mediated insertion compared to unmodified dsDNA. IDT’s proprietary modifications help mitigate that risk when using an Alt-R HDR Donor Block. Second, long ssDNA repair templates can result in incomplete HDR insertions. This does not occur frequently with dsDNA templates such as Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks.
Finally, HDR (homology-directed repair) outcomes may be impacted by foreign DNA of a particular system. While successful HDR has been observed using both products in most systems tested, the ideal donor template may vary with the application and the cell line or system of choice.
The Alt-R HDR Donor Block and Megamer products are both intended to generate CRISPR-mediated insertions. Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks are chemically modified dsDNA repair templates while Megamer Single-Stranded DNA Fragments are long ssDNA repair templates. Megamer fragments are also chemically modified templates, however, their modification is different than that of HDR Donor Blocks. Due to the differences in manufacturing, Megamers are limited in yield (3 µg standard) and can be more costly. Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks are available at larger yields that are typically required for cell culture work (3 or 10 µg standard) and offer a more cost-effective solution. While both products can be used to create CRISPR knock-ins, several differences in repair outcomes have been observed between dsDNA and ssDNA repair templates.
First, ssDNA innately has a lower risk of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) mediated insertion compared to unmodified dsDNA. IDT’s proprietary modifications help mitigate that risk when using an Alt-R HDR Donor Block. Second, long ssDNA repair templates can result in incomplete HDR insertions. This does not occur frequently with dsDNA templates such as Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks.
Finally, HDR (homology-directed repair) outcomes may be impacted by foreign DNA of a particular system. While successful HDR has been observed using both products in most systems tested, the ideal donor template may vary with the application and the cell line or system of choice.
What should I do if my HDR edit did not work?
Editing rates and HDR efficiency can vary significantly from system to system and target to target. Strategies for increased HDR efficiency can include using a guide RNA with robust editing activity, adding the Alt-R™ HDR Enhancer V2, and optimizing donor template design. Some troubleshooting measures are to include a positive control, increase the number of clonal isolates screened, and ensure that the intended edit is not lethal, or being selected against.
Contact us at applicationsupport@idtdna.com for further assistance.
Do I need to include the Electroporation Enhancer in my electroporation experiments if I am also including an Alt-R HDR Donor Block?
The DNA template is typically sufficient to act as a carrier for improved Cas9 delivery, in addition of Electroporation Enhancer may increase cytotoxicity. However, this may require optimization for individual cell lines since the use of Electroporation Enhancer could still benefit some difficult-to-transfect cells.
Does IDT offer larger sizes of Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks?
The sizes of Alt-R™ HDR Donor Blocks currently offered are 3 µg and 10 µg. For large scale requests, contact us directly by emailing genes@idtdna.com.
What are the optimum storage conditions for Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks?
IDT ships Alt-R™ HDR Donor Blocks dry at ambient temperatures. While dry, we recommend long term storage at -20°C. After resuspending in a high quality, molecular-grade water or buffer, pH 7.5-8.0, the Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks should be stored at 4°C for short term, or –20°C for long-term storage. We do not recommend diluting Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks to low concentrations (<10 ng/µL) due to yield loss resulting from adherence of the material to the plastic tube.
How should I resuspend the Alt-R HDR Donor Block?
Follow these steps to resuspend Alt-R™ HDR Donor Blocks:
- Before opening the tube, spin in a microcentrifuge for 3–5 sec to ensure the Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks DNA is in the bottom of the tube.
- Add molecular grade water, or a buffer such as IDTE, to a final stock concentration of
500 ng/µL, or a concentration appropriate for your planned experiment. - Briefly vortex.
- Incubate at approximately 50°C for 20 min. Heating the tube will ensure the water or buffer contacts the tiny pellet, even if it is stuck to the side of the tube. Thus, this step increases the likelihood that the entire pellet will be resuspended.
- Vortex and centrifuge for 3–5 sec. Due to low resuspension volumes required for this product, thorough vortexing or pipetting is recommended to ensure the sides of the tube have been thoroughly exposed to your buffer of choice.
- Verify the final concentration using the NanoDrop™ (Thermo Fisher Scientific), Qubit® instruments (Thermo Fisher Scientific), or another spectrophotometer. Depending on your analysis method, you may want to make a dilution of your sample for the concentration check to conserve material.
Does IDT offer LabReady Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks?
What is the optimal amount of Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks to use with my cell type and what can I do to prevent toxicity and/or cell death after delivering Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks?
Due to recognition of cytosolic dsDNA by innate immune response pathways, careful consideration of the final Alt-R™ HDR Donor Block concentration is necessary to avoid cytotoxicity. We recommend testing for optimal concentrations for each cell line you use, as sensitivity to dsDNA may vary. To learn more, go to the Alt-R Donor Blocks protocol.
Do the universal terminal sequences or modifications on Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks integrate or affect insertion rates?
When the Alt-R™ HDR Donor Blocks are incorporated via the homology-directed repair (HDR) pathway, we have not observed evidence of integration of the universal terminal sequences, or modifications. The modification reduces unwanted non-homologous insertion (blunt integration) events. However, if undesired blunt integration does occur then the universal terminal sequences may be integrated into the genome along with the donor template, but that would be considered a rare event.
How are the Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks modified and does IDT offer custom modifications for Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks?
How are the homology arms for Alt-R™ HDR Donor Oligos and Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks selected by the HDR Design Tool?
For wild-type Cas9, the HDR Design Tool positions one of the homology arms relative to the CRISPR cut site, and the other is positioned relative to the specific mutation site. The default homology arm length for standard single-stranded Alt-R™ HDR Donor oligo designs is 40 bases. The default homology arm length for longer double-stranded Alt-R HDR Donor Block designs is 200 bp. Note that we recommend using homology arms of 200-300 bp. However, homology arms as short as 100 bp can be used if needed due to sequence complexities in the longer homology arm regions.
For nickase designs using single-stranded Alt-R HDR Donor oligos, there are two CRISPR nick sites rather than a single cut site. The mutation is typically located between the two guides, and the homology arms are positioned relative to these two CRISPR nick sites.
Optimal Length for Left & Right Homology Arms?
These factors contribute to the high variability of HDR efficiency observed across different cell lines, and particularly in immortalized cells [2].
While longer inserts are possible, the efficiency of recombination decreases as the insert size increases [3]. Finding successfully integrated inserts is likely to be challenging when inserts are greater than 3 kb in most mammalian cells.
Homology arm length varies based on insert length. IDT's HDR Design Tool will suggest the optimal homology arm length based on the insert size and our empirically supported design rules.
References:
- Elliott B, Richardson C, Winderbaum J, Nickoloff JA, Jasin M. Gene conversion tracts from double-strand break repair in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18(1):93-101.
- Lin S, Staahl BT, Alla RK, Doudna JA. Enhanced homology-directed human genome engineering by controlled timing of CRISPR/Cas9 delivery. Elife. 2014;3:e04766. Published 2014 Dec 15.
- Li K, Wang G, Andersen T, Zhou P, Pu WT. Optimization of genome engineering approaches with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105779. Published 2014 Aug 28.
Biosecurity
Sequence Information is secure and confidential at IDT. Please see our Confidentiality Statement for more information. All online ordering steps, including sequence entry and your choice of parameters, are also secure and protected.
We screen the sequence of every gene, and gene fragment order we receive to (1) identify any regulated and other potentially dangerous pathogen sequences, and (2) verify that IDT’s gene customers are legitimate scientists engaged in beneficial research.
IDT is among the five founding members of the International Gene Synthesis Consortium (IGSC) and helped to create the IGSC’s Harmonized Screening Protocol. The Harmonized Screening Protocol describes the gene sequence and customer screening practices that IGSC member companies employ to prevent the misuse of synthetic genes. IDT takes the steps set out in the Harmonized Screening Protocol to screen the sequences of ordered genes and the prospective customers who submit those orders.
For more information about the IGSC and the Harmonized Screening Protocol, please visit the website at www.genesynthesisconsortium.org.

In October 2010, the United States government issued final Screening Framework Guidance for Providers of Synthetic Double-Stranded DNA, describing how commercial providers of synthetic genes should perform gene sequence and customer screening. IDT and the other IGSC member companies supported the adoption of the Screening Framework Guidance, and IDT follows that Guidance in its application of the Harmonized Screening Protocol. For more information, please see 75 FR 62820 (Oct. 13, 2010), or https://federalregister.gov/a/2010-25728.
RUO21-0385_002.1